Mitosis is a fundamental biological process responsible for growth, development, and tissue repair in multicellular organisms. It involves the division of a single cell into two genetically identical daughter cells. Mitosis plays a critical role in various biological functions, from healing wounds to enabling plants and animals to grow. This article explores which of the steps in this sequence of events is an example of mitosis at work?
which of the steps in this sequence of events is an example of mitosis at work?
Mitosis is a type of cell division that occurs in somatic (non-reproductive) cells. It ensures that each daughter cell receives an exact copy of the parent cell’s genetic material. The process is meticulously organized into distinct phases to maintain cellular integrity and genetic consistency.
which of the steps in this sequence of events is an example of mitosis at work?: Stages of Mitosis
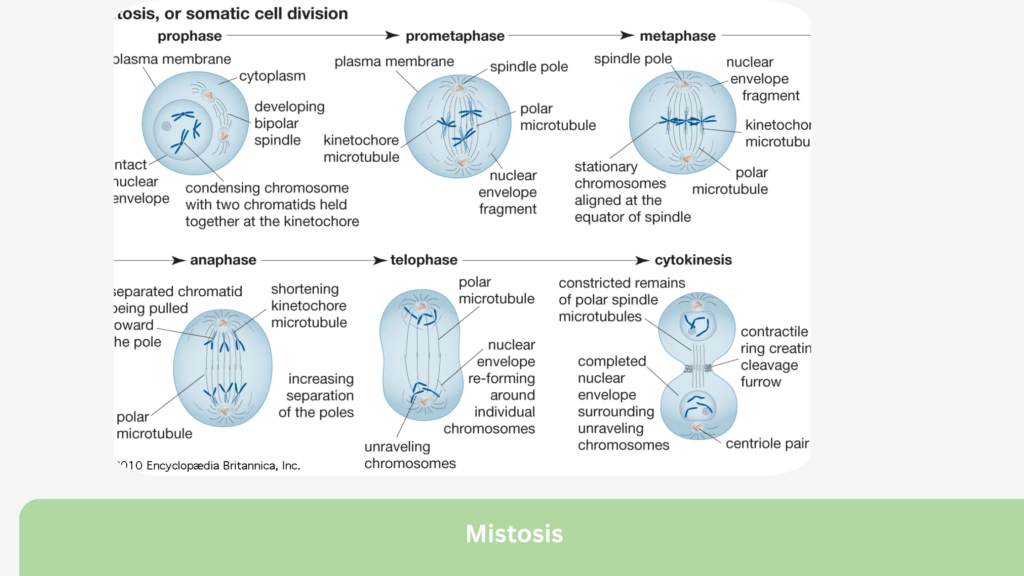
Mitosis occurs in five sequential phases: Prophase, Prometaphase, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophase, followed by Cytokinesis. Let’s delve into each step.
1. Prophase
- The chromatin in the nucleus condenses into visible chromosomes.
- Each chromosome has two identical sister chromatids connected by a centromere.
- The nuclear membrane begins to break down.
- Spindle fibers, essential for separating chromosomes, start to form.
2. Prometaphase
- The nuclear envelope fully disintegrates.
- Chromosomes attach to spindle fibers at their centromeres through protein structures called kinetochores.
3. Metaphase
- Chromosomes align along the metaphase plate (the cell’s equatorial plane).
- This alignment ensures equal separation of genetic material during the next phase.
4. Anaphase
- The centromeres split, and sister chromatids are pulled apart by spindle fibers to opposite poles of the cell.
- This phase ensures each daughter cell will receive an identical set of chromosomes.
5. Telophase
- Chromatids reach the opposite poles and begin to de-condense back into chromatin.
- A nuclear membrane re-forms around each set of chromosomes, creating two nuclei within the cell.
6. Cytokinesis
- The cytoplasm divides, producing two separate daughter cells.
- In animal cells, a cleavage furrow forms to split the cells, while in plant cells, a cell plate develops.
The Role of Mitosis in Biological Processes
Mitosis plays a vital role in various biological events, including growth, repair, and reproduction in certain organisms. Below are some examples where mitosis is at work:
1. Growth and Development
- Mitosis enables multicellular organisms to grow by increasing the number of cells.
- For example, during embryonic development, a single fertilized egg divides repeatedly through mitosis to form a complex organism.
2. Tissue Repair and Regeneration
- When you cut your skin, mitosis is responsible for producing new cells to replace damaged ones.
- In plants, mitosis helps repair damaged leaves or stems.
3. Asexual Reproduction
- In some organisms, such as bacteria and certain plants, mitosis is the primary mechanism for reproduction.
- For instance, in hydras, new individuals are formed by budding, a process reliant on mitosis.
4. Cell Replacement
- In the human body, mitosis continually replaces old or worn-out cells, such as skin cells and blood cells.
- Red blood cells, for example, are replaced approximately every 120 days through mitosis in bone marrow cells.
Examples of Mitosis at Work
Example 1: Healing a Skin Wound
- When the skin is injured, mitosis activates in the basal layer of the epidermis.
- New cells are produced to replace damaged cells, closing the wound over time.
- This is a clear example of mitosis contributing to tissue repair.
Example 2: Plant Growth at Meristems
- In plants, mitosis occurs in regions called meristems, found at root tips and shoot tips.
- Cells divide actively in these regions, allowing the plant to grow taller and roots to extend deeper into the soil.
Example 3: Replacing Stomach Lining Cells
- The stomach lining undergoes constant wear due to digestive acids.
- Mitosis ensures rapid replacement of these cells, maintaining the integrity of the stomach lining.
Example 4: Cancer Formation (Uncontrolled Mitosis)
- While mitosis is essential for growth and repair, errors in its regulation can lead to uncontrolled cell division, forming tumors.
- Understanding mitosis helps scientists develop treatments for cancers by targeting specific stages of the process.
Mitosis vs. Meiosis
Mitosis is often confused with meiosis, but the two processes serve distinct purposes:
| Feature | Mitosis | Meiosis |
| Purpose | Growth and repair | Reproduction |
| Number of Divisions | One | Two |
| Result | Two identical daughter cells | Four genetically unique cells |
| Occurs in | Somatic cells | Germ cells |
President Biden Pardons Hunter Biden: A Controversial Decision Sparks National Debate
Importance of Mitosis in Everyday Life
1. Health Maintenance
Mitosis is crucial for maintaining the body’s health by replacing dead or damaged cells, such as in the skin, blood, or internal organs.
2. Agricultural Advancements
Understanding mitosis aids in enhancing crop yields by promoting controlled cell growth and repairing plant injuries.
3. Medical Innovations
Research on mitosis has paved the way for cancer therapies, regenerative medicine, and tissue engineering.
Conclusion
Mitosis is an essential biological process that ensures the continuity of life by creating new cells. From healing wounds to facilitating growth and development, mitosis plays a pivotal role in the functioning of living organisms. By understanding this process, scientists and medical professionals continue to find innovative ways to improve human health and address challenges like cancer.
Whether in a laboratory or in everyday life, examples of mitosis at work are all around us, ensuring the survival and evolution of species.